SpaceX’s Starship is the Ultimate American Dream: A Race Against Time and China to Reclaim Lunar Supremacy and Forge a New Era of Space Exploration that Could Define Our Future as a Nation and a Species, Challenging the Status Quo of Traditional Aerospace!
SpaceX’s recent update on its contract with NASA to land astronauts on the Moon has ignited a fierce debate about the future of lunar exploration and the role of private companies in space. As the United States faces increasing competition from China, which is making significant strides in its own lunar ambitions, the stakes have never been higher. SpaceX’s bold claims about its Starship program and its potential to fulfill NASA’s Artemis program vision have raised eyebrows and questions about the efficacy of traditional aerospace contractors and government-led initiatives.
The Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon for the first time since the last Apollo mission in 1972, represents a significant shift in NASA’s approach to space exploration. It is designed not only to land astronauts on the lunar surface but also to establish a sustainable human presence there. This ambitious goal is seen as a stepping stone toward future missions to Mars, which is the ultimate objective for SpaceX and its founder, Elon Musk. Musk’s vision of colonizing Mars has been a driving force behind the company’s innovations and its relentless pursuit of technological advancements.
However, Musk has been vocal in his criticism of the Artemis program, labeling it as unambitious and overly reliant on established aerospace contractors. This criticism reflects a broader sentiment within the space industry that traditional methods and bureaucratic processes are hindering progress. SpaceX, with its rapid development cycles and innovative approach, positions itself as a disruptive force capable of accelerating lunar exploration and paving the way for Mars colonization.
The urgency of the situation is underscored by the growing perception that China may soon achieve a crewed lunar landing, potentially before the United States. China’s lunar program has made remarkable advancements, including successful robotic missions and plans for a crewed lunar landing in the near future. This has raised alarms within the U.S. space community, as the prospect of being outpaced by a rival nation in such a critical area of exploration could have far-reaching implications for national pride, technological leadership, and geopolitical standing.
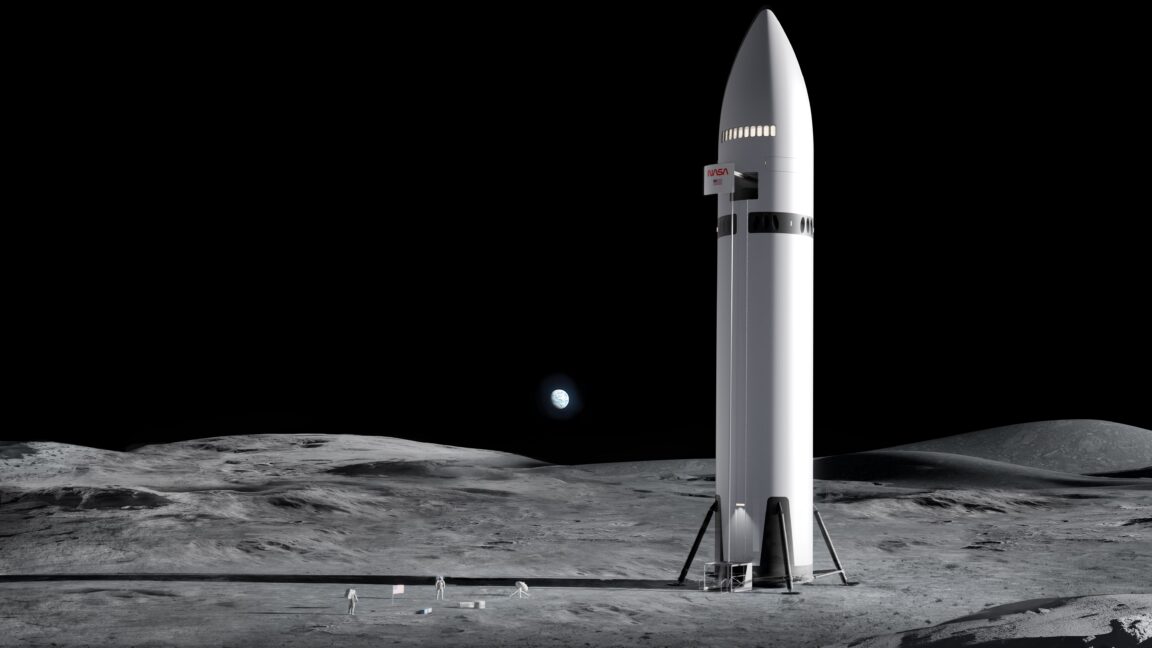
In its recent statement, SpaceX emphasized its role as a “central enabler” of the Artemis program, asserting that its Starship vehicle will be instrumental in achieving the program’s goals. The company has invested billions into the development of Starship, which is designed to be a fully reusable spacecraft capable of carrying large payloads and crew to various destinations, including the Moon and Mars. This ambitious vehicle is seen as a game-changer in the space industry, with the potential to significantly reduce the cost of access to space and enable more frequent missions.
The implications of SpaceX’s success extend beyond just lunar exploration. The company’s vision of a human presence on Mars has captured the imagination of many and has the potential to redefine humanity’s relationship with space. Musk’s goal of making life multi-planetary is not just a lofty aspiration; it is a mission that could inspire a new generation of scientists, engineers, and explorers. However, achieving this vision requires overcoming numerous technical, financial, and logistical challenges.
As the competition for lunar supremacy heats up, the question remains: can SpaceX deliver on its promises and help the United States reclaim its leadership in space exploration? The answer to this question will not only shape the future of NASA’s Artemis program but also influence the trajectory of human exploration beyond Earth. The stakes are high, and the world is watching as SpaceX and its rivals race to the Moon and beyond, with the potential to alter the course of history in the process.
The dynamics of international competition in space exploration are complex and multifaceted. The United States has long been viewed as a leader in space, but the emergence of China as a formidable competitor has prompted a reevaluation of strategies and priorities. The space race is no longer solely about technological prowess; it encompasses economic, political, and strategic considerations that could have lasting implications for global power dynamics.
In this context, SpaceX’s role as a private entity operating within the framework of a government contract raises important questions about the future of public-private partnerships in space exploration. The collaboration between NASA and SpaceX has the potential to leverage the strengths of both entities, combining the innovative capabilities of a private company with the resources and expertise of a government agency. However, this partnership also highlights the challenges of navigating bureaucratic processes and ensuring accountability in a rapidly evolving industry.
As SpaceX continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in space travel, the company’s relationship with NASA and its ability to meet the ambitious timelines set forth by the Artemis program will be closely scrutinized. The success or failure of these missions could have profound implications for public perception of space exploration, funding for future initiatives, and the overall direction of U.S. space policy.
The narrative surrounding lunar exploration is not just about technological advancements; it is also deeply intertwined with national identity and aspirations. The Moon has long been a symbol of human achievement and exploration, representing the pinnacle of scientific and engineering accomplishments. As nations vie for dominance in this arena, the implications extend beyond the realm of science and technology, touching on themes of nationalism, pride, and the human spirit’s relentless quest for discovery.
In conclusion, the race to the Moon is not merely a contest of technological capabilities; it is a reflection of humanity’s aspirations and the desire to explore the unknown. As SpaceX positions itself as a key player in this endeavor, the world watches with bated breath, eager to see how this new chapter in space exploration unfolds. The outcome of this race will shape not only the future of lunar exploration but also the trajectory of human civilization’s journey into the cosmos.
SpaceX on Thursday released the most detailed public update in nearly two years on its multibillion-dollar contract to land astronauts on the Moon for NASA, amid growing sentiment that China is likely to beat the United States back to the lunar surface with humans.
In a lengthy statement published on SpaceX’s website Thursday, the company said it “will be a central enabler that will fulfill the vision of NASA’s Artemis program, which seeks to establish a lasting presence on the lunar surface… and ultimately forge the path to land the first humans on Mars.”
Getting to Mars is SpaceX’s overarching objective, a concise but lofty mission statement introduced by Elon Musk at the company’s founding nearly a quarter-century ago. Musk has criticized NASA’s Artemis program, which aims to return US astronauts to the Moon for the first time since the last Apollo lunar mission in 1972, as unambitious and too reliant on traditional aerospace contractors.